Companies used to spend countless hours and money on asset tracking and inventory management because this was all done by hand. Manual tracking not only took a painstakingly great amount of work hours, but it also allowed there to be a greater risk for mistakes and human error. RFID technology has greatly helped many industries like retail, manufacturing, and hospitality with operations such as warehouse management.
With the introduction of RFID technology, companies can efficiently and accurately track shipments, products, or entire skids without having to be in direct line-of-sight of the product.
What is RFID Technology?
RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification and is a technology that uses radio waves to communicate wirelessly to locate and identify a variety of objects. RFID technology allows the tags to be read using the reader device wirelessly, allowing companies to scan multiple tags simultaneously.
RFID is governed by different regulations, such as RAIN and NFC, which are industry-supported technologies.
There are many RFID systems available, and understanding the RFID regulations and standards will help guide you in choosing the best-suited RFID solution for your company. Businesses need to understand the industry regulation of RFID technology and how that may impact their business.
RFID technology is governed by guidelines and stipulations on how it is used and developed. These regulations dictate how the systems will work, the transference of data, what frequencies are used, and the communication between the tag and the reader device.
Why Do RFID Regulations Matter?
RFID regulations are in place to provide continuity of operations, no matter what user or vendor is used. These standards also give guidance to companies looking to develop altered software, tags, accessories, or readers.
RFID standards also help to drive up competition and broaden the market, which in turn brings the costs of RFID products down. Having standards in place gives consumers peace of mind and confidence in this technology.
RFID tags store product information and data and dictate the communication process between the tags and the tag readers. The tag frequency that is used for the tag will determine what standards are applied for low-frequency, high-frequency, or ultra-high-frequency tags.
Who Develops RFID Regulations?
RFID regulations and standards are created and issued by trade-specific regional, national, and global groups, such as the International Standards Organization (ISO) and GS1. ISO and GS1 work collectively to support RFID standards for worldwide specifications regarding RFID technology equipment.
Worldwide implementation is feasible for RAIN RFID by developing universal standards. Increasing standardization not only helps explain RFID’s competencies but it ensures seamless integration with other systems within a company. In turn, this will help reduce costs by increasing competition and broadening the market for RFID products.
The Federal Communication Commission (FCC) oversees the frequency bands that are for RFID in the United States, while other regions are regulated through other entities. As advances in RFID technology and applications are developed, the goal is that more opportunities for RFID tag use will be available to both companies and consumers on a global scale.
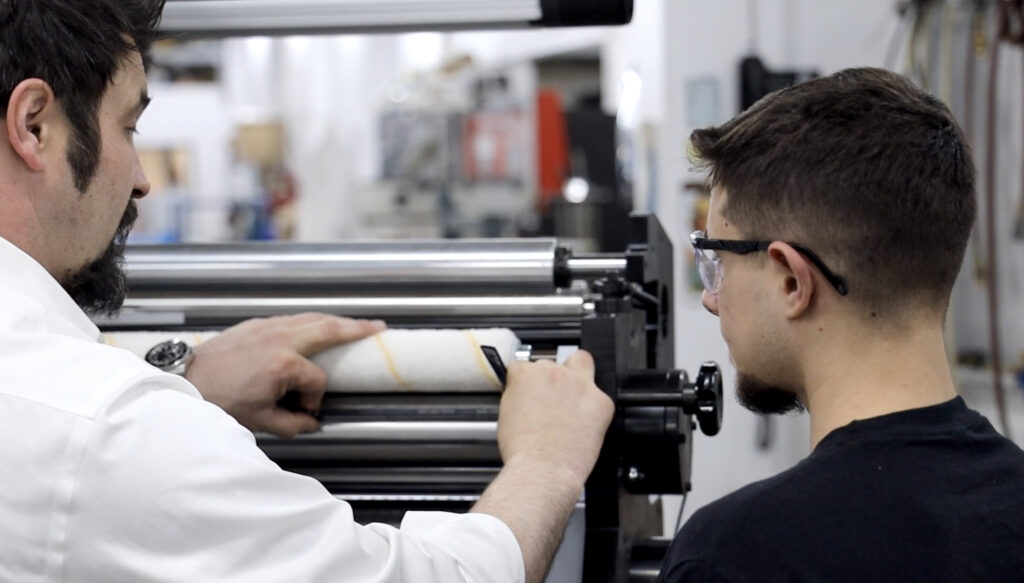
Tamarack® Products has been a renowned industry leader for over 50 years, providing customers with high-quality and reliable web-finishing equipment. We offer RFID technology solutions that are customizable and fully scalable with easy integration into your existing flexo press. Our MVW Inline inlay insertion system is servo-driven for an easy setup featuring operator-friendly controls.
Tamarack® Products will design, engineer, and manufacture top-quality finishing equipment that is customized to meet your business needs. Our MVW Inline allows packaging converters an easy web path to incorporate RFID technology seamlessly and quickly. Contact us for more information on the numerous advantages of implementing RFID technology for your product and packaging needs.